
April 30, 2025
Crying Without a Reason: Understanding Neonatal and Infant Colic
Hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) is a viral infection that causes a rash or blisters on the hands and feet, as well as in or around the mouth. There are two types of viruses that cause HFMD, and the symptoms vary depending on the virus.
HFMD mainly affects children under the age of 10, but can also affect adolescents. It spreads easily from one person to another. It is possible to contract the virus more than once, but the symptoms will be less severe.
The viruses that usually cause hand-foot-and-mouth are named coxsackievirus a16 and enterovirus 71.
Signs :
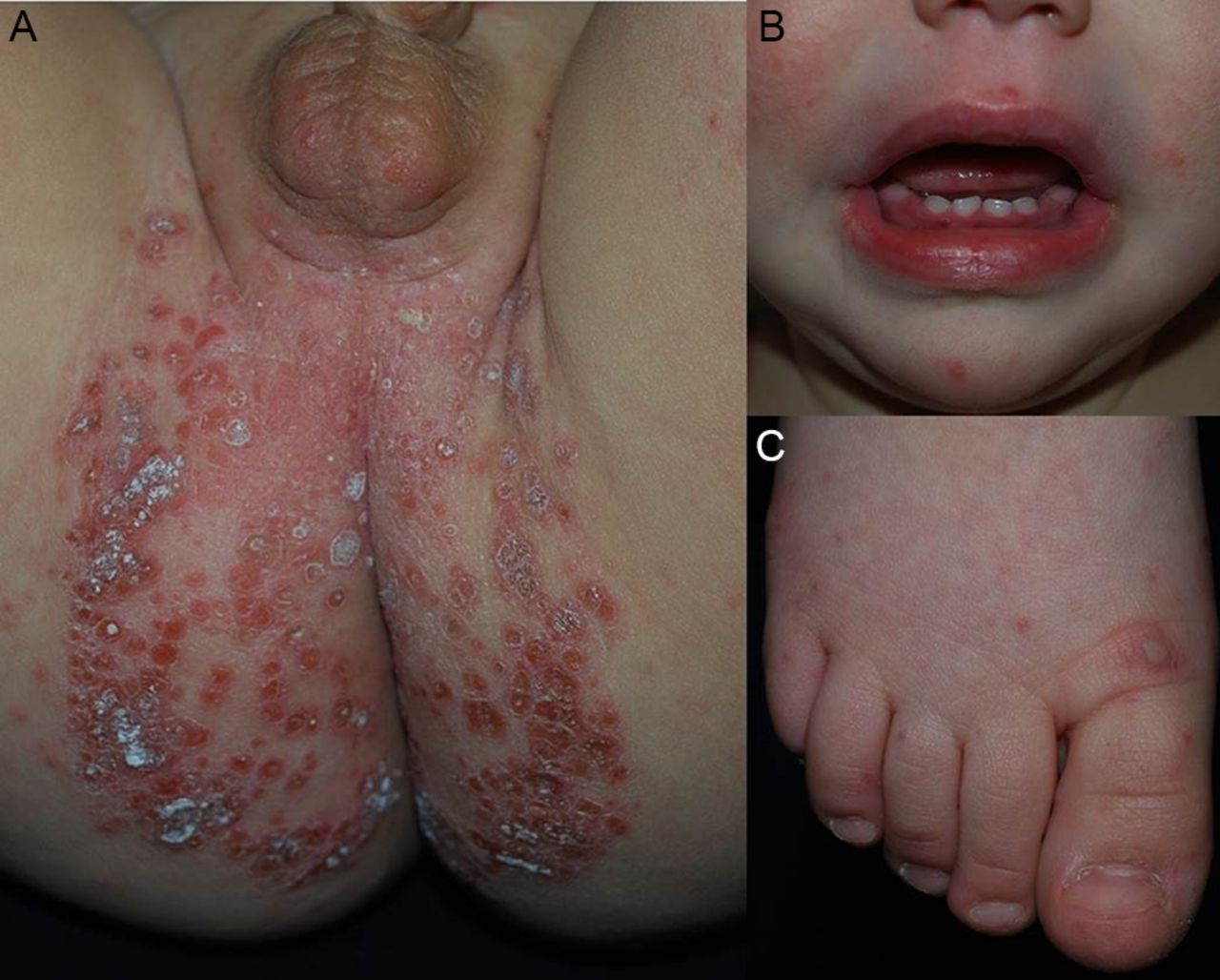
Early symptoms may include fever and a sore throat. Painful blisters similar to cold sores can show up on the inside of your child’s mouth or on his tongue.
He might get a rash on the palms of his hands or the soles of his feet a day or two after the first symptoms appear. This rash may turn into blisters. Flat spots or sores may pop up on the knees, elbows, or buttocks. He could have all of these symptoms, or only one or two.
Mouth sores can make it hurt to swallow, so be sure your child gets enough water and calories.
Prevention :
HFMD is most commonly caused by the coxsackie virus. The main way HFMD spreads is through contact with the fluid from inside the blisters, or with the droplets spread from sneezing and coughing. The virus can also be present in bowel movements (poo) for up to several weeks after the person has recovered.
To prevent the spread of HFMD:

Leave a comment